|
|
Mediastinal Teratoma
Dermoid
- Mediastinum is a
rare site for occurrence of teratomas, most being ovarian in origin
- Arise from
primitive germ cell rests
- Supposed to
migrate along urogenital ridge to primitive gonad
- Journey is
interrupted in the mediastinum
- May be solid or
cystic
- Three
major categories
- Mature teratomas
- Well-delineated from surrounding tissues
- Contain ectodermal elements along with cartilage, fat and smooth
muscle
- Immature teratomas
- Same elements as above with primitive tissues found in fetus
- Teratomas with malignant transformation
- Overall about 30% are malignant
- Usually adenocarcinoma in mature teratomas
- Angiosarcoma or rhabdomyosarcoma in immature teratomas
- Most of the cystic lesions are benign and most of the solid lesions are
malignant
- Both occur
early in life—young adults most commonly
- DDX from
thymomas which usually occur in 5th or 6th decade
- Symptoms
- Usually
asymptomatic
- Large lesions
can cause shortness of breath, cough or retrosternal pain or fullness
- Rare rupture of
dermoid into trachea which leads to trichoptysis—expectoration
of hair
- Associations
- Non-lymphocytic
leukemia and malignant histiocytosis with immature teratomas
- Imaging findings
- Most occur in
the anterior mediastinum, near junction of great vessels and
heart
- Benign lesions are usually smooth in contour whereas malignant
masses tend to be lobulated
- Usually larger than thymomas
- Calcification
may rarely occur but is of no
help since thymomas also calcify
- Exception
would be the very rare occurrence of a tooth or bone in a dermoid
- CT shows fatty
mass with globular calcifications and rarely a tooth or bone
- Fat-fluid
level may be seen on CT
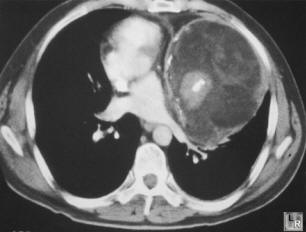
Enhanced CT scan of the chest shows large, septated
anterior
mediastinal mass containing fat and bony elements
- Rapid increase in
size may mean hemorrhage into a cyst rather than enlarging malignancy
- Treatment and
prognosis
- Mature teratomas
- For benign
cystic teratomas, surgical resection
- Excellent
prognosis
- Immature
teratomas
- In childhood,
surgical excision is often successful
- In adults,
tend to have a more malignant course
- Teratomas with
malignancy
- Usually highly
aggressive
- Poor prognosis
- Teratoma versus
dermoid
- Dermoid contain only epidermis
- Teratomas contain all 3 germ layers, but are mostly endodermal when
malignant
- Other germ cell
neoplasms
- Benign dermoid cysts
- Benign and malignant teratomas
- Seminomas
- Choriocarcinomas
- Embryonal cell carcinomas
- Mediastinal seminomas
- Rare
- Almost always in
young men
- Identical to
testicular seminoma and ovarian dysgerminoma
- May be well-encapsulated or invasive
- Tends to be lobulated
- Cannot be
differentiated from teratoma
- Primary choriocarcinoma
- Even rarer than
seminoma in the mediastinum
- Only 23 reported
in the literature, almost all in men
- Occur between
20-30 years
- May be lobulated
- May have
elevated beta sub unit of HCG
- Growth is very
rapid leading to dyspnea, hemoptysis, stridor
- Gynecomastia and
a + Aschheim-Zondek test can occur
- Rapidly fatal

Mediastinal Teratoma. Contrast-enhanced axial CT scan of the chest demonstrates an anterior mediastinal mass containing calcification (black arrow), fat (white arrow) and soft tissue components (dotted white arrow).
For this same photo without the arrows, click here
For more information, click on the link if you see this icon 
Fraser and Pare
|
|
|